Gastric Banding Surgery
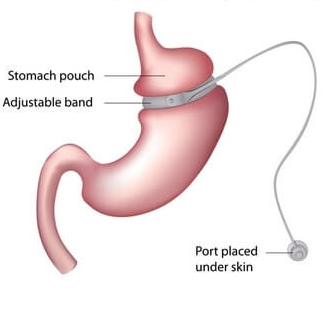 The procedure is performed through laparoscopy. It involves placing a silicone adjustable gastric band around the upper part of the stomach, reducing its functional size and emptying time; leaving a reservoir of about 20 to 30 ml as a new stomach.
The procedure is performed through laparoscopy. It involves placing a silicone adjustable gastric band around the upper part of the stomach, reducing its functional size and emptying time; leaving a reservoir of about 20 to 30 ml as a new stomach.
The band has three parts: the adjustable band itself, a port or reservoir, and a flexible tube that connects both.
The band has a soft, inflatable balloon on the inside that can be filled with saline solution to tighten or loosen its grip. The port or reservoir is placed on the left side of the patient´s body, under the skin, so adjustments can be made by injecting or removing fluid, in order to open or close the band and allow or restrict the passage of food from the pouch to the stomach. A tube connects the port to the band so that liquid can flow. Adjustments are made every two to three months depending on weight loss and patients' satiety effects.
The purpose of the adjustable gastric banding procedure is to induce early satiety, allowing feelings of fullness after eating small portions of food. The total amount of ingested calories will be diminished and the patient will gradually lose weight, leading to a healthier life, and diminishing the risks of obesity related health conditions.
The placement of the adjustable gastric band is framed in the context of a comprehensive treatment for obesity, since it does not lead to progressive and permanent weight loss by itself. This means that the patient will be asked to follow a diet plan and exercise program in order to obtain the best results from the treatment.
This technique is fully reversible since no anatomical alteration of the stomach is performed, allowing for the band to be removed if necessary.
Is Gastric Banding for Me?
To be considered a candidate for gastric banding surgery, patients must meet or exceed a BMI of 35. Because BMI is not accurate for everybody, patients who are at least 100 pounds overweight are considered good candidates for gastric banding surgery. Patients who are severely obese, patients whose BMI is over 45, are not qualified candidates like this the recommendation would be gastric bypass surgery.
Patients are also expected to have co-morbidities that are threatening to the patient. Co-morbidities including type two diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, are examples of things that look favorable during the surgeon’s review of your health history.
POSTOPERATORY NUTRITION PROGRAM
The adaptation stage corresponds to the first 6 weeks after surgery. The main issue is the “consistency” of the foods which is required because the most important objective is to take care of the position of the band. It is very important to follow every advice regarding the ingestion of food to make sure the position and functioning of the band are correct.
Not following indications the first 30 days will cause abdominal pain and vomiting which will put at risk the position and proper functioning of the band.
The main point in the adaptation stage is proper nutrition. Within the feeding process there are several issues which are important to ensure optimum results of the treatment:
The patient needs to follow all the instructions about the quantity and consistency of foods that we recommend for each period. Ninety eight percent of the cases of postoperative problems like epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, or movement of the band occur because patients do not follow instructions regarding consistency of foods.
The distribution of foods has to include all three food groups, this is necessary to obtain a nutritional balance. The patient must get used to cooking without oil and sweetening with artificial diet sweeteners. Adding up the caloric control to the decrease in the amount of food consumed and daily exercise, better and quicker results will be obtained. After the band is adjusted, most cases for not losing weight are due to poor quality of foods and to an increase in calories per meal.
A schedule has to be followed to maintain order, with specific hours to have meals, three meals are required per day: breakfast, lunch and dinner; each one following the characteristics recommended. If any extra food is needed, between meals, a non fat meal is recommended.
1. Eat slowly
2. Chew very well all foods
3. Take small bites (30% or 40% of what used to be normal)
4. Stop eating when you start feeling full
5. Do not drink liquids at the same time you eat solids (just take small drinks to moisten the food if desired)
- 90% of post-operatory vomiting is caused by improper eating techniques.
- 10% of post-operatory vomiting is caused by a band that is too tight






Comments are closed.